Capital Gains and Losses
How do you net capital gains and losses?
Ø How do you net capital gains and losses?
Quick answer when taxpayer only has short term and long-term capital gains/losses:
Short-term loss offset short-term gain, then long-term loss offset long-term gain, then you net those two together.
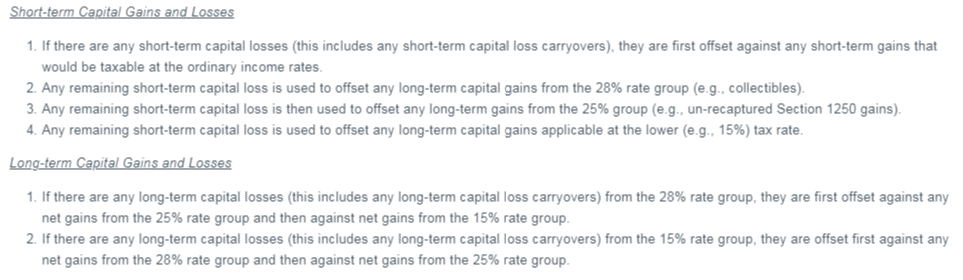
In Depth Ordering rules for short-term capital losses:
· Reduce short-term capital gains
· Reduce net long-term gains taxed at 28%
· Reduce net long-term gains taxed at 25%
· Reduce net capital gain taxed at 20%, 15%, or 0%.
In Depth ordering rules for long-term capital losses:
· Net capital losses from 28% rate assets reduce long-term gains taxed at 25%, then long-term gains taxed at 20%, 15%, or 0%.
· Net capital losses from 20%, 15% or 0% rate assets reduce long-term gain taxed at 28%, and then reduce long-term gain taxed at 25%
Ø How long can you carry forward capital losses?
Capital losses are carried forward indefinitely, until the taxpayer dies.
Ø What are the maximum long term federal capital gains rates?
Depending on taxable income of the taxpayer, Long Term capital gains are taxed at 0, 15 or 20%. An additional 3.8% Net Investment Income Tax is applied to certain high-income taxpayers.
Ø Who is subject to the 3.8% Net Investment Income Tax?
The Net Investment Income Tax went into effect starting with the 2013 tax year. It is imposed by section 1411 of the Internal Revenue Code and applies to individuals, estates and trusts. It is a surtax, calculated and added to regular and other taxes.
For individuals, the tax is applied at a rate of 3.8% to the lesser of:
Net investment income or Modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) above the statutory threshold amounts:
Single - $200,000
MFJ - $250,000
Head of Household - $200,000
MFS - $125,000
Ø Can I gift a capital loss to someone else?
Capital losses cannot be gifted. If an asset with a loss in it is gifted to someone, that will create a dual basis in the asset which ultimately takes away that loss.
Example: If a stock is purchased at $50 and is gifted away when it is trading at $40, if the person who received the stock then sells it for $38 they will only realize a $2 loss. The $10 loss it had when it was gifted is gone.
Pub 551 page 9
Ø How will a long-term capital gain impact my AMT situation?
Long-term capital gains still are taxed at preferential rates under AMT. However, if a significant capital gain is realized, the taxpayer may lose some of their AMT exemption which could in turn make them subject to AMT.
Ø How do I report multiple sell transactions on my tax return?
Individual transactions are reported on IRS Form 8949.
Ø How are collectibles taxed?
Short-term collectibles are taxed at ordinary income rates, and collectibles held long-term are taxed at a maximum 28% tax rate. For long-term collectibles if the ordinary income rate is lower than 28%, the taxpayer will pay the lower rate.
Gold, art, http://www.irs.gov/taxtopics/tc409.html
http://www.spdrgoldshares.com/usa/faqs/#q4fa24b4ed7055
Ø How is the sale of Qualified Small Business Stock (QSBS) taxed?
A portion or all the gain (depending on when acquired) from the sale of QSBS stock is excluded from gross income if held for more than 5 years. The taxable portion of the gain is included in income as long-term capital gain subject to a 28% rate.
QSBS acquired 08/11/1993 – 02/17/2009 is eligible for a 50% gain exclusion
QSBS acquired 02/18/2009 – 09/27/2010 is eligible for a 75% gain exclusion
QSBS acquired on or after 09/28/2010 is eligible for a 100% gain exclusion.
Note: The amount of your gain from the stock of any one issuer that is eligible for the exclusion is limited to the greater of:
Ten times your basis or
10 million (5 million if MFS)